Structure and Application of Vacuum Furnace
2024-07-05
What is a vacuum furnace?
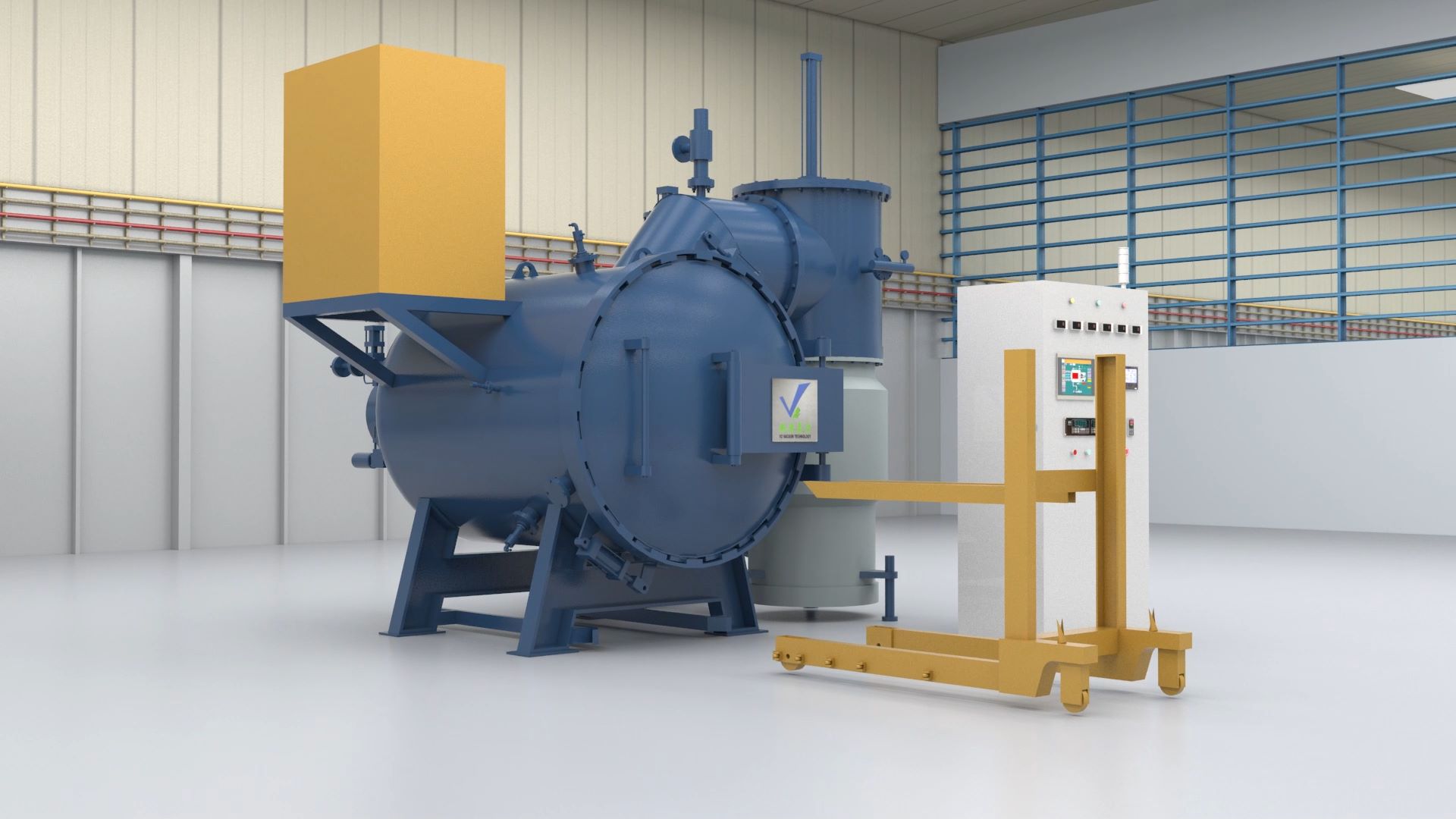 A vacuum furnace is a type of furnace in which materials (usually metals) are heated to very high temperatures and processes such as soldering, sintering and heat treating are performed with high consistency and low contamination. In a vacuum oven, the product in the oven is surrounded by a vacuum. The absence of air or other gases prevents heat transfer to the product by convection and eliminates sources of contamination.
A vacuum furnace is a type of furnace in which materials (usually metals) are heated to very high temperatures and processes such as soldering, sintering and heat treating are performed with high consistency and low contamination. In a vacuum oven, the product in the oven is surrounded by a vacuum. The absence of air or other gases prevents heat transfer to the product by convection and eliminates sources of contamination.
The advantages of vacuum furnaces include:
1. ability to control temperature in a small area
2. low content of carbon, oxygen and other gases that pollute the product.
3. rapid cooling (hardening) of the product.
4. Possibility of computer control of the process to ensure metallurgical repeatability.
Heating metals to high temperatures usually results in rapid oxidation, which is undesirable. Vacuum ovens remove oxygen and prevent this process. Inert gases (such as xenon) are often used to quickly cool the metal being processed to non-metallurgical levels after the required furnace treatment. The inert gas can be pressurized to twice atmospheric pressure and then circulated in the hot zone, absorbing heat, which is then removed by a heat exchanger. This process continues until the desired temperature is reached.
Vacuum furnace structure: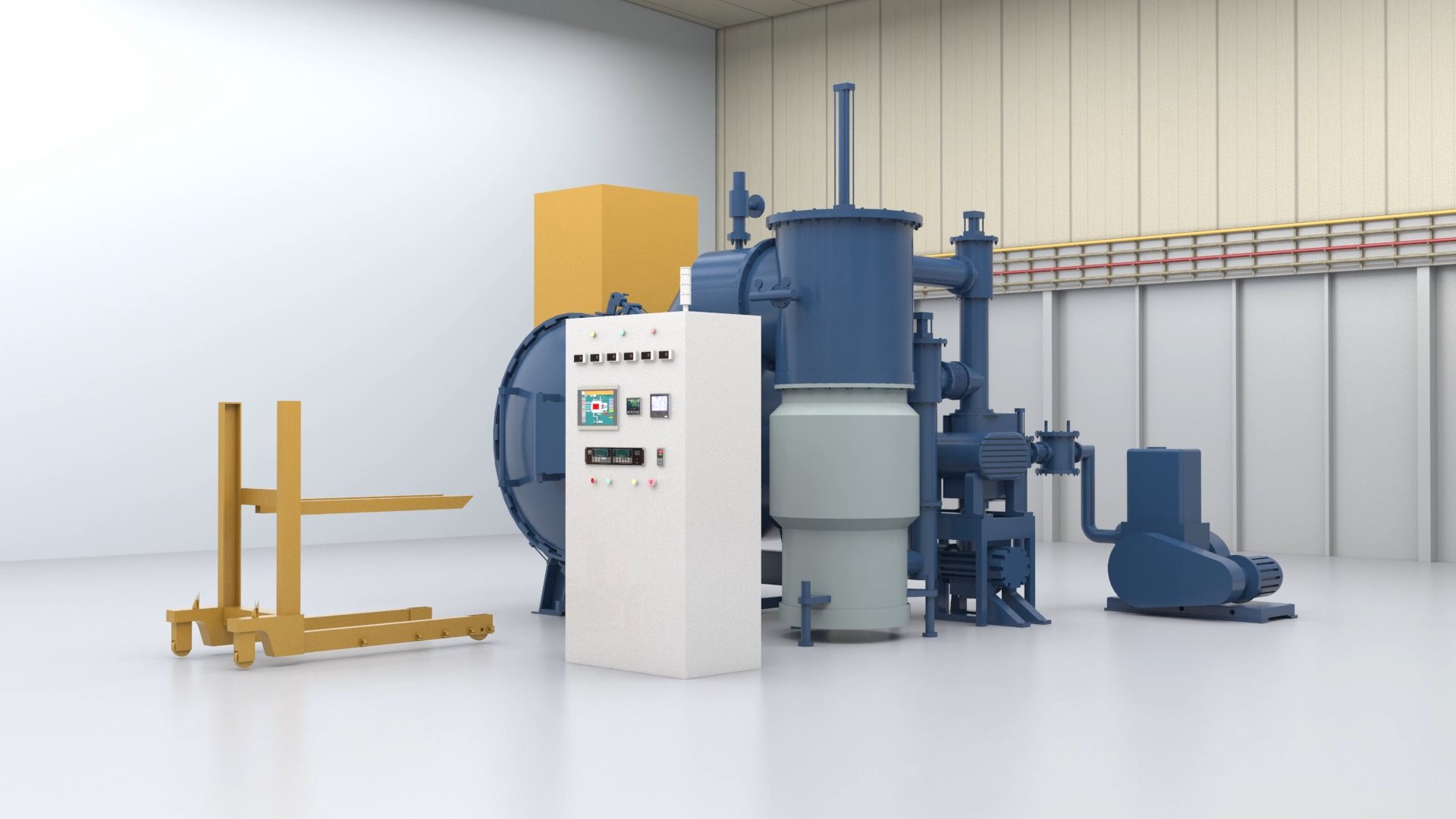
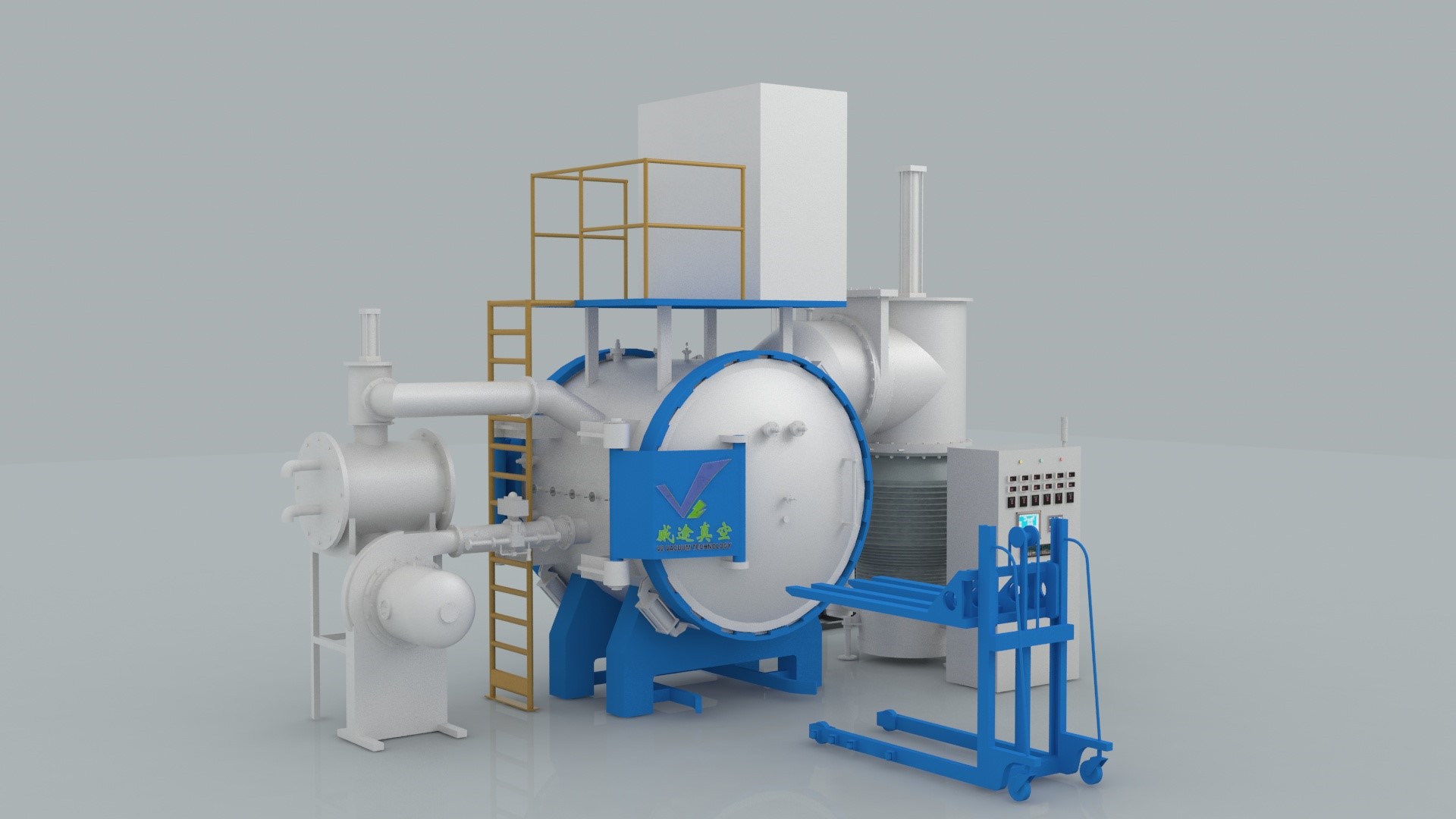
The vacuum furnace is composed of furnace body, vacuum unit, hydraulic system, control system, cooling system and other parts. For a gas-cooled vacuum furnace, a nitrogen storage tank must be provided. To prevent water outages or insufficient water pressure, an overhead water reservoir must be installed to prevent burning or erosion of seals and electrodes due to water outages. The body and door of the vacuum furnace are made of high-strength sheet steel, welded and pressed. It is a double water jacket structure, and the vacuum furnace door is opened and closed by rack and pinion drive. It is flexible and comfortable. The heating chamber adopts a circular structure, the graphite tube heater and the cooling gas nozzle are evenly distributed around the heating chamber 360 degrees. High quality carbon felt and flexible graphite paper are used as insulation materials. The structure is light and durable. According to the heating form, the vacuum furnace can be divided into two types: external heating type and internal heating type. The internally heated furnace is the preferred type for vacuum furnace manufacturers. According to different structure, can be divided into single chamber, double chamber, three chamber and continuous straight vacuum furnace. There are dual-purpose furnaces with gas cooling, oil cooling and gas-oil cooling. True air hardening can be performed on stainless steel, high-alloy cast steel, high-speed tool steel, and iron-nickel alloys using ammonia gas of 99.999% purity or higher.
Heating materials used in vacuum furnace.
Heating elements of vacuum furnaces are divided into metal and non-metal.
1. Metal heaters are generally divided into two types: one is precious metals, such as molybdenum, platinum, tungsten, tantalum, etc., and the other is general metals, such as nickel-chromium high-temperature alloys, iron-chromium-aluminum alloys , molybdenum-tungsten alloys and so on.
2. non-metallic heaters – graphite and composite. The composition of the composite includes silicon carbide, molybdenum silicide, molybdenum dioxide, etc. Silicon carbide easily decomposes at high temperatures, and molybdenum dioxide softens at 1300 degrees. Only graphite has the characteristics of good machinability, high temperature resistance, good quenching resistance, good ductility, large radiating area, good thermal shock resistance, so it is suitable for making heat generator.
Operating principle of a vacuum furnace.
A vacuum furnace uses the phase change of water in a hot environment for heat exchange. The heat released during fuel combustion is absorbed by the coolant water. When the temperature rises to the saturation temperature of the vacant state, evaporation occurs to a saturation and vapor state, and the first phase transition process is completed. The flow of condensate into the evaporation chamber continues to absorb heat, completing the phase change cycle. The lower structure of the direct air hot water boiler consists of a combustion chamber and a bundle of heat exchange tubes; upper part of the vacuum chamber, inserted U-tube heat exchanger; The vacuum chamber is connected to the pumping unit to maintain the stability of the vacuum chamber, pumping out non-condensable gases inside the vacuum chamber to improve the heat transfer efficiency of the U-tube heat exchanger.
Application of Vacuum Furnace
1. Vacuum hardening (tempering, annealing) is a method of heating and cooling materials or parts in a vacuum in accordance with technological protocols to achieve the desired properties.
2. Vacuum brazing is a welding process in which a group of welds is heated under vacuum to the melting temperature of the filler metal, but below the melting temperature of the base material. (Soldering temperature depends on the material.)
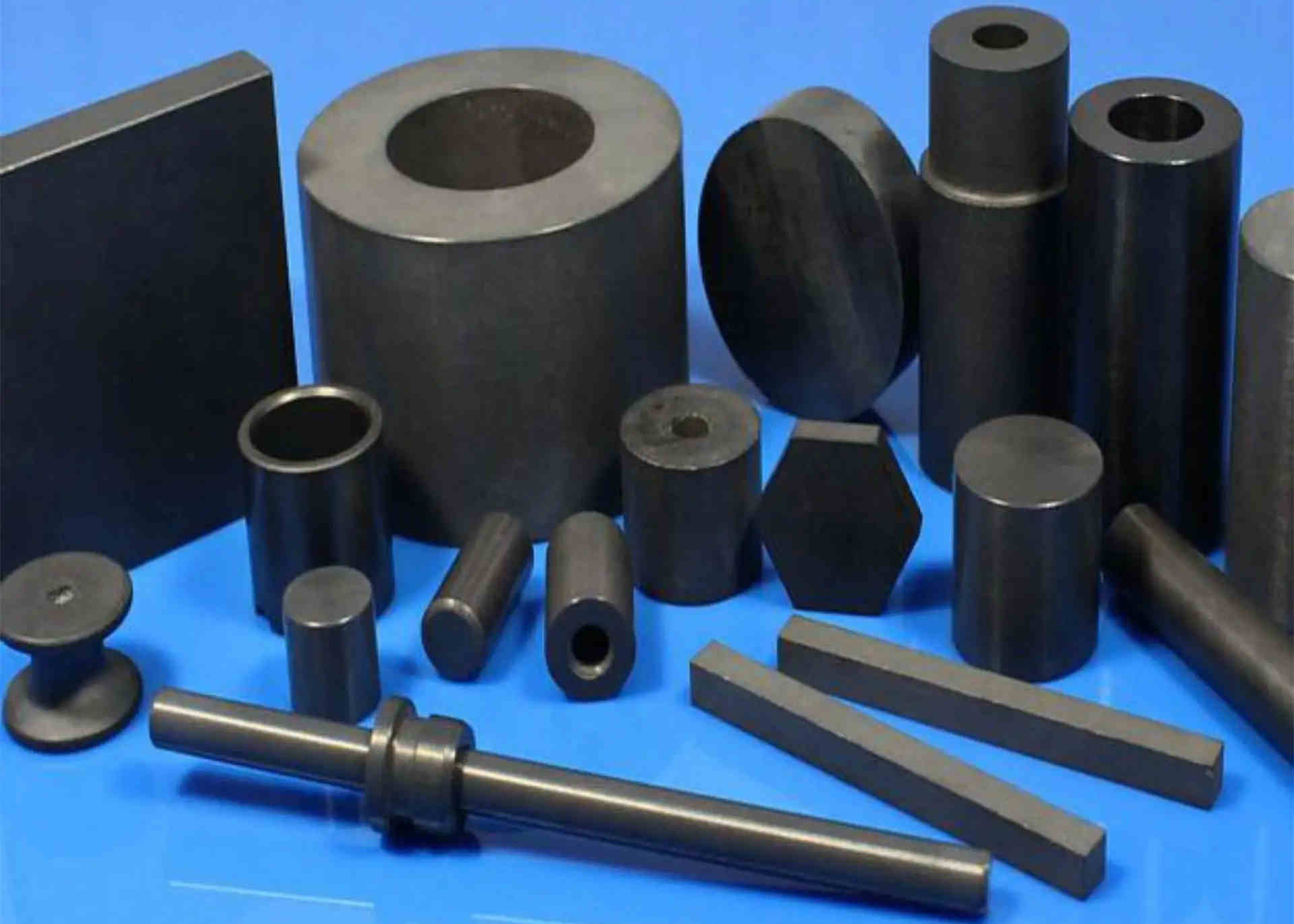
3. Vacuum sintering is a method of sintering adjacent metal powder particles into a part by adhesion and diffusion by heating the metal powder product in a vacuum.
4. Vacuum magnetization is mainly used for metal materials processing and magnetization.






